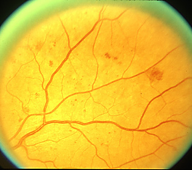
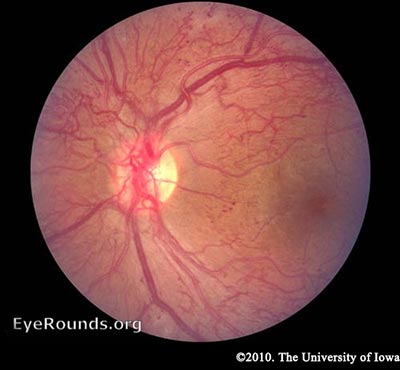
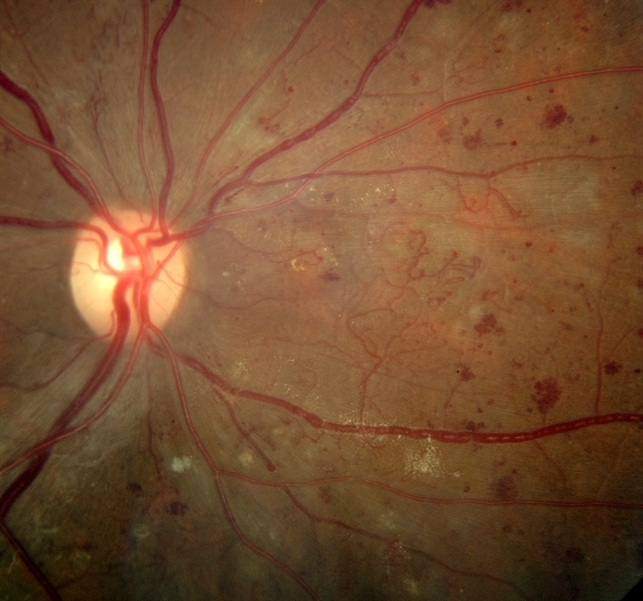
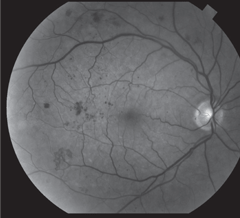
Severe NPDR , IRMA visible inferonasally Condition/keywords nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy Siegrist Streak Nov 6 12 by F Ryan Prall, MD 32yearmale with history of hypertension, recent admission for malignant hypertension Photographer Tom Egnatz, Indiana University Retina Image BankApr 28, 21 · In two eyes, NVE originated from sea fan IRMA Ten eyes images were classified as IRMA only with no FFA leak, or ILM breach The relation of preretinalApr 03, 14 · In this paper a method for automatic detection of blood vessels in retinal image is described Here a method for blood vessel detection based on pixel classification using a 7D feature vector extracted from preprocessed retinal images 3 With the use of pixels, an image is divided into many parts by declaring each image pixel to the nearest
Q Tbn And9gctzmoe2bpyacukr Vafqm6hjeil4ksunjrpuha6gxqmfpngcfyo Usqp Cau
Irma retina images
Irma retina images-Courtesy of O Lezoray, Cherbourg Institute of Technology, University of Caen RBC and IRMA databases courtesy of T Deselaers and T Lehmann, RWTH chen Retina images courtesy of Retinal Cell Biology Laboratory & Center for BioImage Informatics, UCSBMar 15, 17 · Fig 3 (A) This color en face OCTA image shows a combination of retinal layers in an eye with a choroidal neovascular membrane (B) Shows the segmentation boundaries and color codes for each of the individual en face OCTA images below The en face OCTA images are the superficial retina (D) the deep retina and (E) avascular



Community Eye Health Journal Recognising And Managing Diabetic Retinopathy
The EyePACS digital retinal grading protocol evaluates the presence and severity of the discrete retinal lesions associated with diabetic retinopathy The lesions graded are microaneurysms (MA), retinal hemorrhages with or without microaneurysms (HMA), cotton wool spots (CW), intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA), venousAug 24, 17 · Retina, Vitreous Bayoneting of vessels and beanpot cupping in advanced glaucoma Glaucoma, Iris Bilateral Cranial Nerve VI Palsies Secondary to Arachnoid CystSep 01, · In this, Intra Retinal Microvascular Abnormalities (IRMA) is one of the important factors IRMA is the abnormal branching or expansion of retinal blood vessels The rules in grading DR are mentioned in Table 1 DR in its serious phase is hard to heal It will result in complete vision loss Local features of retinal images are extracted
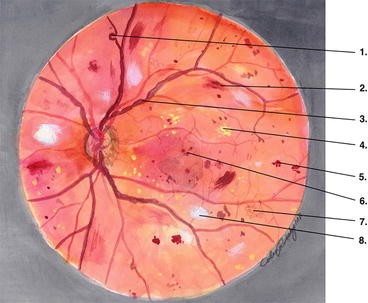
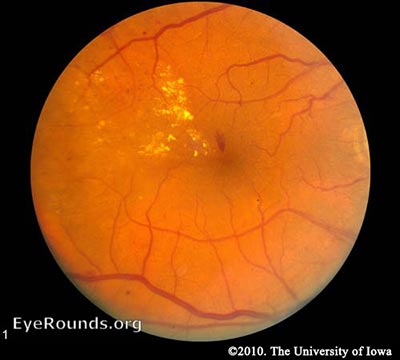
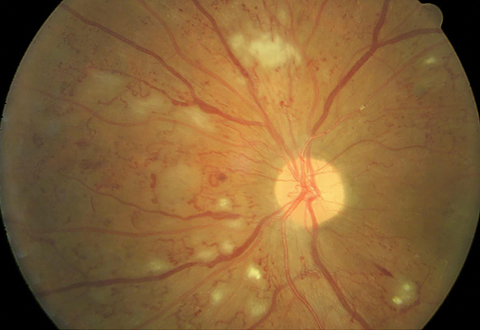
The given retinal image is preprocessed using Dualistic SubImage Histogram Equalisation The method first decomposes an input image into two subimages based on the median of the input image One of the subimages is the set of samples less than or equal to the median whereas the other one is the set of samples greater than the medianImages Diabetic retinopathy Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy intraretinal microvascular abnormality (IRMA;Green arrow), venous beading and segmentation (blue arrow), cluster haemorrhage (red circle), featureless retina suggestive of capillary nonperfusion (white ellipse) Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive;
Intra retinal micro vascular abnormalities (IRMA) B Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is recognized by severe damage to retina's blood vessels and reduction in flow of oxygen to retina III PROPOSED METHODOLOGY In this work the retinal images are first preprocessed andRegions suspicious for IRMA or retinal NV were identified and the OCTA, including flow overlay on the coregistered structural optical coherence tomography, and fluorescein angiography images were graded by two masked readers Results Ninetysix foci of irregular vasculature were analyzed, comprised of 70 IRMA and 26 retinal NV lesions from 14In this chapter, the authors use an edge detection technique to extract and segment blood vessels in the retinal image They propose a novel approach to detect vessels in a simulated light fields fundus image, based on the image representation with the first and the second order derivative, well known as gradient and Laplacian image descriptors



The Finger Classification Of Radiation Retinopathy New York Eye Cancer Center



Discussion And Pictures Of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions
Red free and from artefacts by viewing on overlapping images where possible IRMA should not be recorded unless visible on colour images, without enlarging the image area, in addition to red free images The macula is defined as that part of the retina which lies within a circle centred on theWith 45, 50 or 60 ° being typical Images are usually rectangularRetinal images are acquired by a specialized camera called fundus camera Mydriatic and nonmydriatic fundus cameras are used for retinal photog raphyThe imaging modalaties are fundus film based (IRMA) and neovascularization,retinal oxymetry , facilitate localization of retinal and disc pathology 6 Adaptive optics SLO Greater degree of



The Usual Retina Suspects Modern Optometry



Community Eye Health Journal Recognising And Managing Diabetic Retinopathy
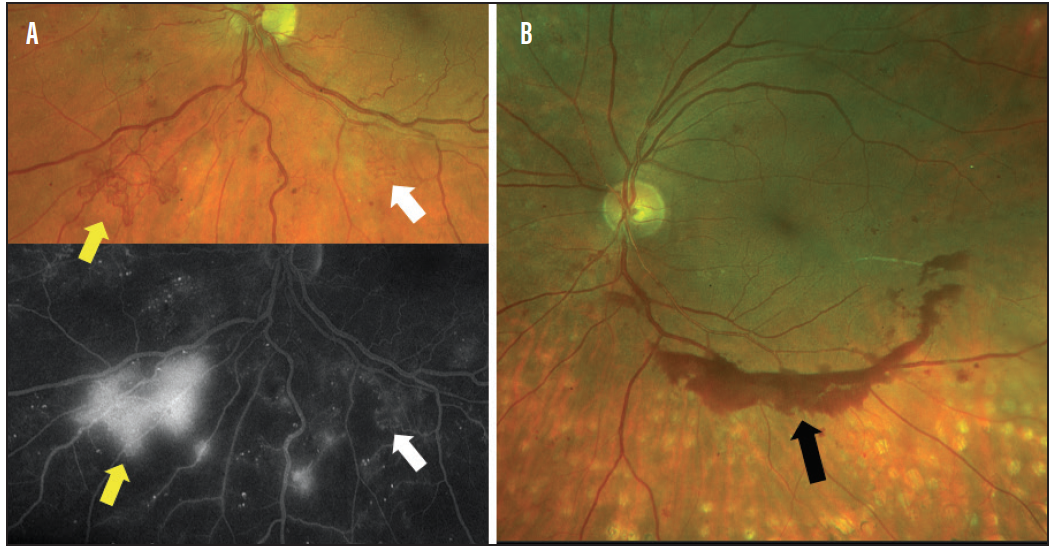
Figure 9 (A) Color images of right eye of patient with diabetic retinopathy previously treated with laser (examples of pigmented laser spots shown by arrows) (B) Fluorescein angiogram of same eye showing intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (arrow) and areas of avascular retina with dilated capillaries, an irregular foveal avascular zone, and microaneurysms (arrowhead)Sep 19, 17 · Misplaced fluid is a hallmark of exudative retinal disease We have directly seen this flooding qualitatively for decades with fluorescein angiography In this issue, Jaya Kumar, MD, and Justis Ehlers, MD, outline their vision of automated, quantitative assessment of widefield angiographic features such as leakage, microaneurysms and nonperfusionNov 04, 15 · If your thinking what the heck is the difference between IRMA (intraretianl microvascular abnormalities) and NVD (neovascularization of the disk), or NVE (neovascularization everywhere else) you are not alone For help distinguishing between them Usually the IRMA is within the retina and does not occur on the disk It is much more discrete, darker in



Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Springerlink



Q Tbn And9gct7yikh Zvyd Naziqhj2d8ifbhm2w M7jyqcyhtkwlaafdifg1 Usqp Cau
Regions suspicious for IRMA or retinal NV were identified and the OCTA, including flow overlay on the coregistered structural optical coherence tomography, and fluorescein angiography imagesRetinal imagers evaluated UWF images for referable DR at the time of image capture Training of the imagers included 4 h of standardized didactic lectures and 12 h of guided image reviewJun 01, · Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a common complication of diabetes and is a major contributor to vision impairment globally The worldwide prevalence of DR is rapidly increasing, and is expected to cause visual deterioration in more than 6 million patients in the US by 30 Intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMAs) are a common finding in the eyes of diabetics




Severe Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy With Intra Retinal Download Scientific Diagram



Discover Images Retina Image Bank
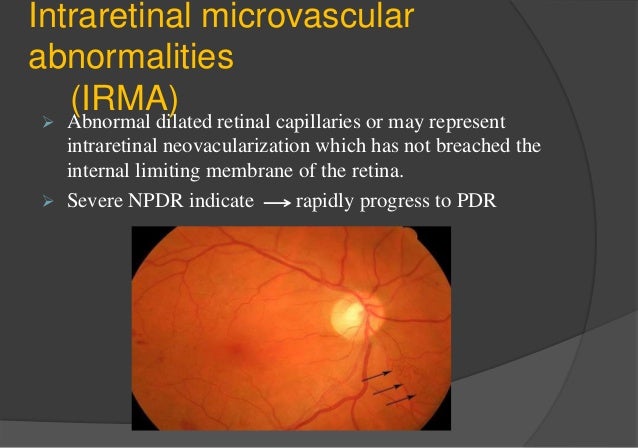
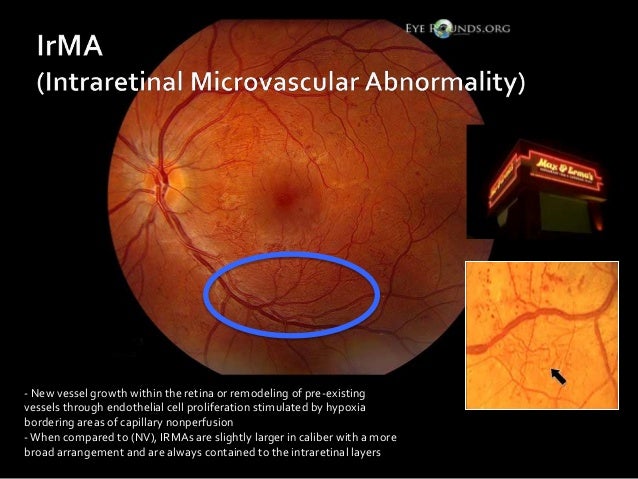
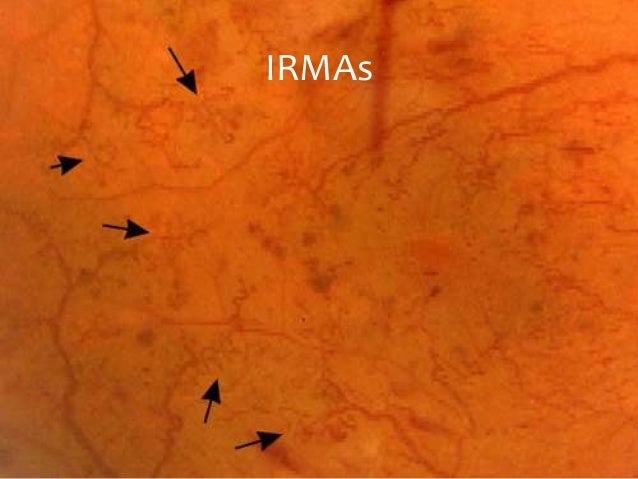
DRS 7field retinal photography I Originated from an NIH funded diabetic retinopathy research group beginning in the 1970's II Provides for standardized grading scales that are reproduceable across readers III Requires stereo pairs for each field (28 images in a full imaging study) IVIdentification of retinal neovascularization and intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA) is crucial in management of diabetic retinopathy as these features define highrisk diabetic retinopathy Two features of OCTA imaging enhance its ability to characterize IRMA and retinal neovascularization widefield OCTA and flow overlayIntraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities (IRMA) Intraretinal microvascular abnormalities are shunt vessels and appear as abnormal branching or dilation of existing blood vessels (capillaries) within the retina that act to supply areas of nonperfusion in diabetic retinopathy



Diabetic Retinopathy For Medical Students Classification




Figure 1 From Diabetic Retinopathy Stage Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks Semantic Scholar
OCT image of a 42yearold male patient with a localized traction of the superior macula secondary to proliferative diabetic retinopathy Imaging device Cirrus Condition/keywords retinal detachment, tractional retinal detachmentRetina with diabetic retinopathy (DR), in this case, microaneurysms (Ma), retinal hemorrhages, and intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA), against the retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) background These two images represent diametrically opposed interests the polar bear does not want to be seen (especially by a seal!), while theThe lowest level of agreement was associated with IRMA;




Intraretinal Microvascularabnormalities Irma The Clinica Flickr



Diabetic Retinopathy Europe American Academy Of Ophthalmology
FUNDING NOTICE The Glycosmedia website and newsletter has been made possible with funding support from our sponsors None of our sponsors have control over the content of the website, newsletter, apps, Twitter feed or RSS newsfeedHowever the physical locations of these lesions are in the very exterior layer of the retina (in the nerve fiber layer) Cotton Wool Spots often occur in association with IRMA (discussed below) Figure 4The information contained here should be used as a general guidance when viewing opto map images The differential diagnosis should be made under the direction of the responsible physician These images were taken on a variety of ultrawidefield opto map devices The images in this section are all color opto map images Pathology




Intra Retinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irma Recognizing Pathology Optos



Diabetic Retinopathy Grading And Classification Eyesteve Com
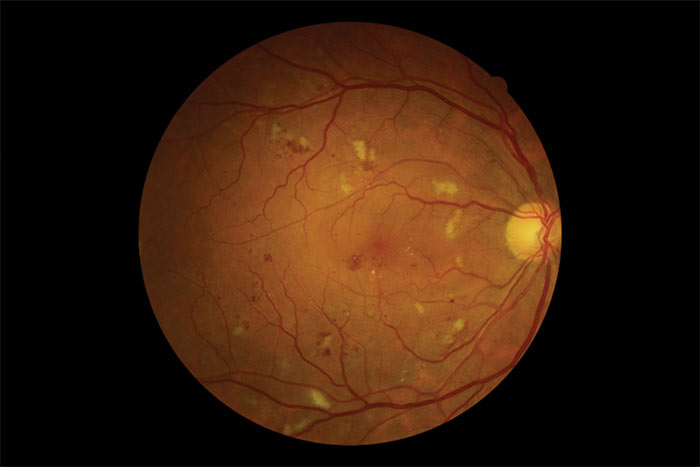
Intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA) are abnormalities of the blood vessels that supply the retina of the eye, a sign of diabetic retinopathyIRMA can be difficult to distinguish from and is likely a precursor to retinal neovascularizationOne way to distinguish IRMA from retinal neovascularization is to perform fluorescein angiographyDiabetic retinopathy can lead to severe vision loss secondary to diabetic macular edema, tractional retinal detachment from fibrovascular proliferation, macular ischemia and complications from neovascular glaucoma OCT has increased the sensitivity to detect diabetic macular edema and track progression of treatment from focal/grid laser and antiVEGF therapiesDec 01, · Except most often at the posterior pole of the retina, MA, IRMA, and NPA were also reported to be more prevalent in the superior temporal , nasal 4, 12, 13, temporal , or midperipheral 10, 21 retina on the basis of experimental work in diabetic animals and human autopsy specimens, or by using ETDRS 7standard 30degree stereoscopic color



Diabetic Retinopathy



Diabetic Retinopathy For Medical Students Classification
SE's physically represent infarcts, or closures of capillaries, within the retina;Nov 03, 15 · Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormality (IrMA) Intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (or IrMAs) are shunt vessels and appear as abnormal branching or dilation of existing blood vessels (capillaries) within the retina that act to supply areas of nonperfusion in diabetic retinopathy These vessels represent either new vessel growth within theIntraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA) and new vessel growth To build an expert system that is able to perform the diagnosis task needed to use digital retinal images By imaging the retina of a person with a special camera, then using image processing and pattern recognition technique to analyses that




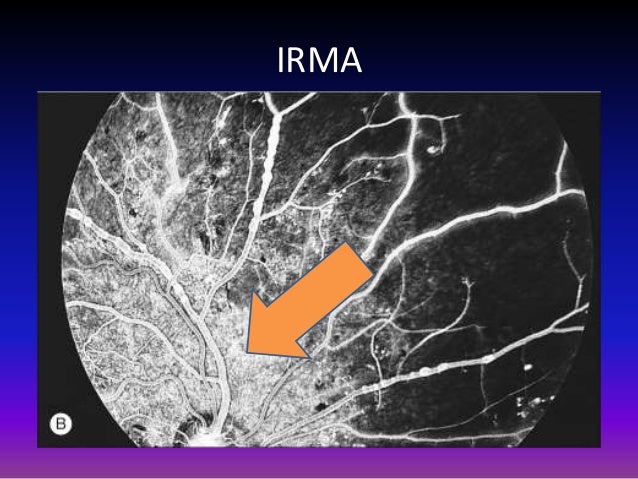
Analysing Vascular Structure To Determine Intra Retinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irma Semantic Scholar




Retinal Image That Exhibits Venous Beading And Irma Caused Due To Download Scientific Diagram
Jun 29, · IRMA originated from and drained into a retinal venule, arising from the inner plexiform (67%), ganglion cell (17%) or nerve fiber layers (17%) 19, 25 These hyperreflective structures were intraretinal, frequently extending across more than one layer and without ILM breach 14, 16, 21, 24,25,26, 30, 31, 38,39,40,41, 59, 65May 11, 16 · Adenocarcinoma of the retinal pigment epithelium Adenocarcinoma of the retinal pigment epithelium wth focal invasion of the choroid Adenoid cystic carcinoma Capillary hemangioma specimen from a child Choroidal melanoma Choroidal melanoma Histopathology reveals the sclerostomy (arrow) through which the retrobulbar melanoma was formed ChoroidalRetinal images of all examined participants aged 40 years and older who had a vertical CDR 06 or greater were regraded in 12 (IRMA), from the worse eye IRMA are retinal collateral vessels in areas of retinal ischemia indicating a more severe level of retinopathy This variable is coded using the ETDRS photo standard, 8A



Diabetic Retinopathy



Diabetic Retinopathy Grading And Classification Eyesteve Com
May 10, 21 · Two 45° field images using the Canon CR2 digital fundus camera were taken per eye, one image centred on the optic disc and the other centred on the macula (imageRegions suspicious for IRMA or retinal NV were identified and the OCTA, including flow overlay on the coregistered structural optical coherence tomography, and fluorescein angiography images were graded by two masked readersDiabetic retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes, affects the blood vessels in the retina (the thin lightsensitive membrane that covers the back of the eye) It is due to the retina not receiving enough oxygen If untreated, it may lead to blindnessIf diagnosed and treated promptly, blindness is usually preventable



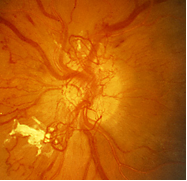
Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities And Venous Beading Retina Image Bank




Intra Retinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irma Recognizing Pathology Optos
Abbreviations or Slang with similar meaning ERDJ4 Microvascular Endothelial Differentiation Gene 1 IRMA Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities RMEC Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cell AAT abnormalities of all type AIMC abnormalities of increased myeloproliferation in childhood AND Abnormalities on DiffusionA collection of pictures on diabetic retinopathy Pictures of Diabetic Retinopathy (The following pictures can also be found at the relevant sections of the guidelinesSmall, isolated IRMA present on two images were missed from 41 KB images This was the case in one JPEG00 image








Diabetic Retinopathy Features Of Diabetes Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irmas
Are required Lesions of the retinal capillaries, such as micro aneurysms and intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA) require this resolution for unequivocal assessment Digital image acquisition is usually over a larger field of view;Sep 08, 12 · Detection of IRMA was especially higher for all the observers with redfree images The only retinal lesion for which color images scored marginally better was for the detection of hard exudates Table 1 is a summary of the lesions detected by the three observers




What Is The Difference Between Irma And Neovascularization Nve Example One Images Questions About Diabetes Related Retinopathy



Ctscans



Q Tbn And9gctzmoe2bpyacukr Vafqm6hjeil4ksunjrpuha6gxqmfpngcfyo Usqp Cau



Discussion And Pictures Of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions



Diabetic Retinopathy A Clinical Survival Guide



Community Eye Health Journal Recognising And Managing Diabetic Retinopathy




Diabetes Flashcards Quizlet




Optometric Management Unveil Retinal Vascular Disease Through Octa




Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Retinal Physician Pearls For Treating Patients With Diabetic Retinopathy




Topic Assignment Medical Ophthalmology Ppt Video Online Download
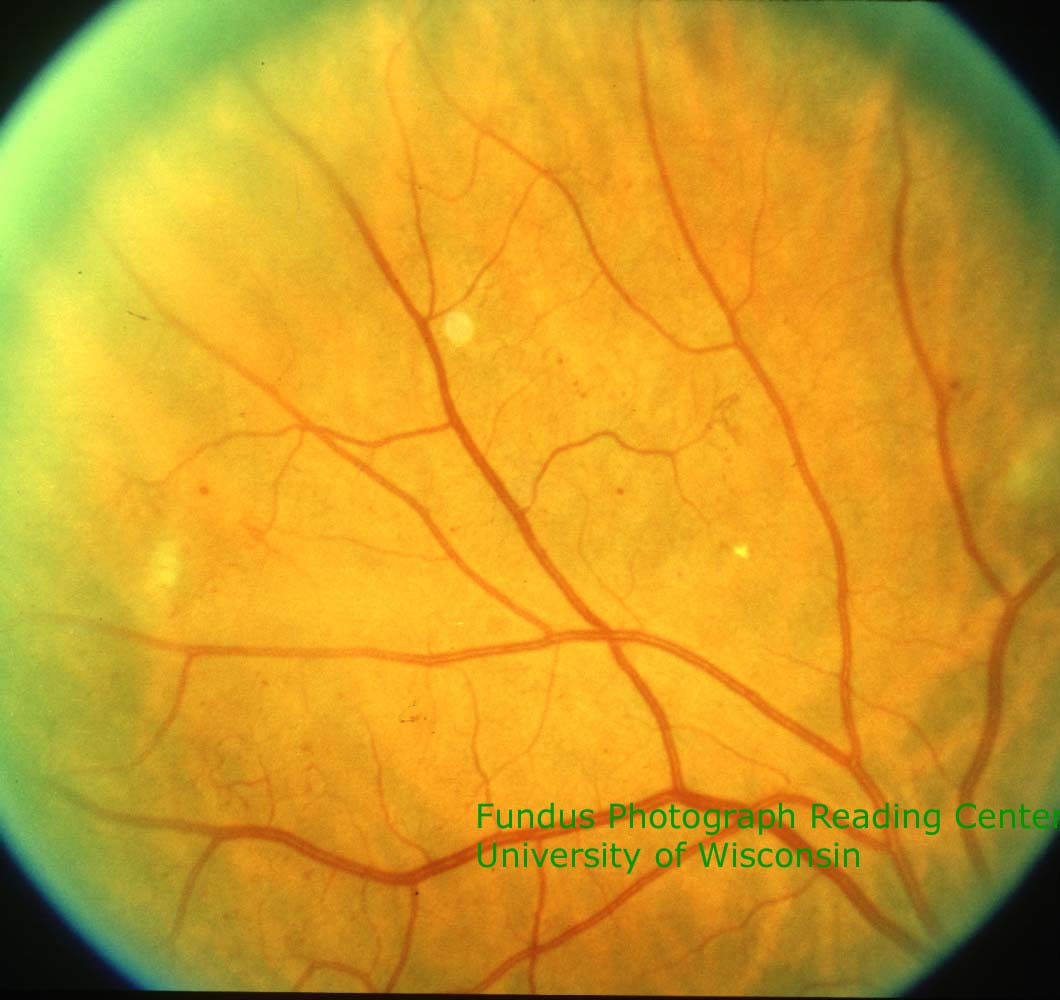



Eyepacs Digital Retinal Image Grading



Community Eye Health Journal Recognising And Managing Diabetic Retinopathy



Diabetic Retinopathy Grading And Classification Eyesteve Com



Diabetic Retinopathy By The Numbers



3




Interpreting Photographs Issuu




Pathogenesis Classification And Treatment Of Diabetic Retinopathy Eyes On Eyecare



Diabetic Eye Screening Services In Scotland A Training Handbook July 03 Page 9




Intra Retinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irma Recognizing Pathology Optos




Hich Brings Us To Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes Aid



Diabetic Retinopathy Grading And Classification Eyesteve Com




Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopahty Npdr Columbia Ophthalmology



Www Coavision Org Files 6 diabetic retinopathy monterey 17 ho Pdf
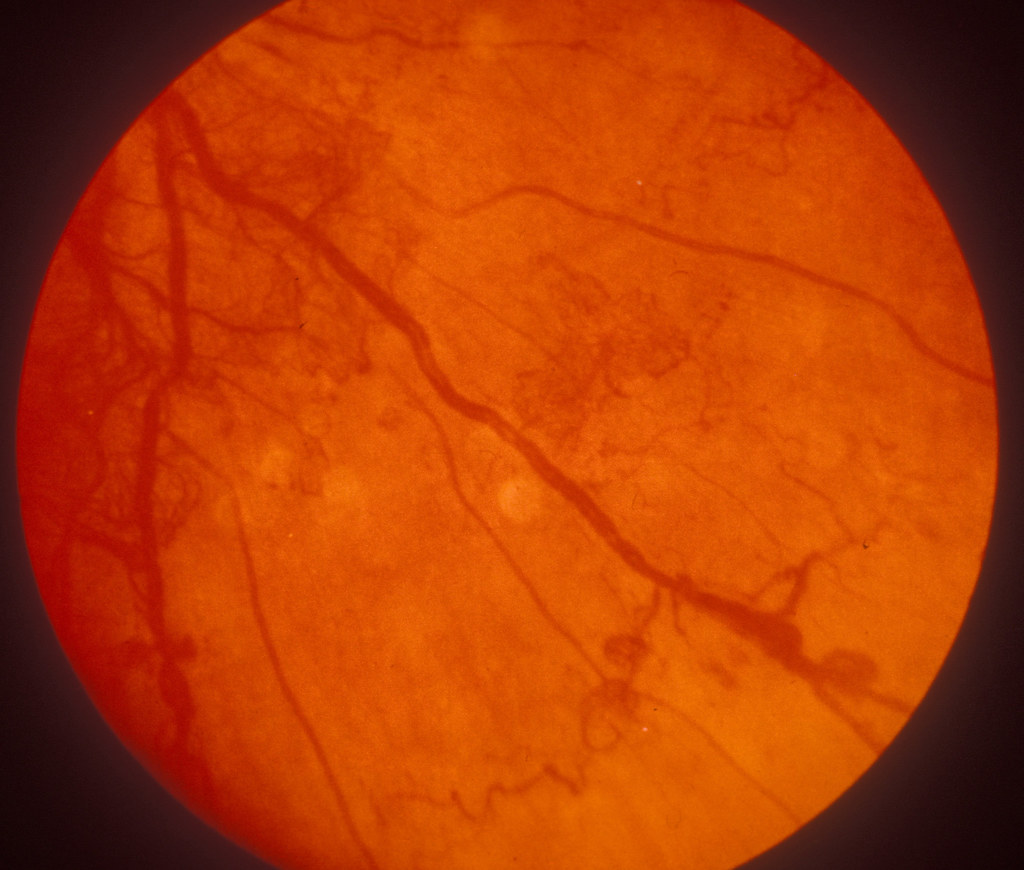



Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy With Irma C Clare Gilbe Flickr
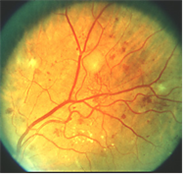



Discussion And Pictures Of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions



Using Oct Angiography To Diagnose High Risk Diabetic Retinopathy Retina Today




Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Ratio Is Improved When Using A Digital Nonmydriatic Fundus Camera Onsite In A Diabetes Outpatient Clinic




Histological Evidence Of Remodelling In The Diabetic Retina A A Download Scientific Diagram



Www Eyepacs Org Consultant Clinical Grading Eyepacs Digital Retinal Image Grading Pdf




Retinal Images With Irma A Presence Of Irma In The Image Was Not Download Scientific Diagram
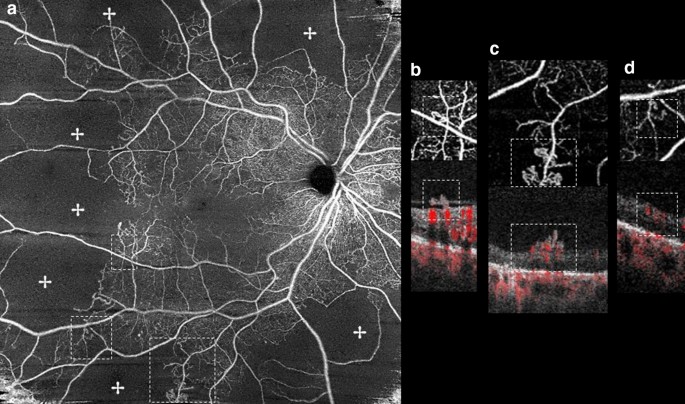



Optical Coherence Tomography Features Of Neovascularization In Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy A Systematic Review International Journal Of Retina And Vitreous Full Text




M R Akhlaghi Md It Is Based On Ophthalmoscopic Signs Ppt Download
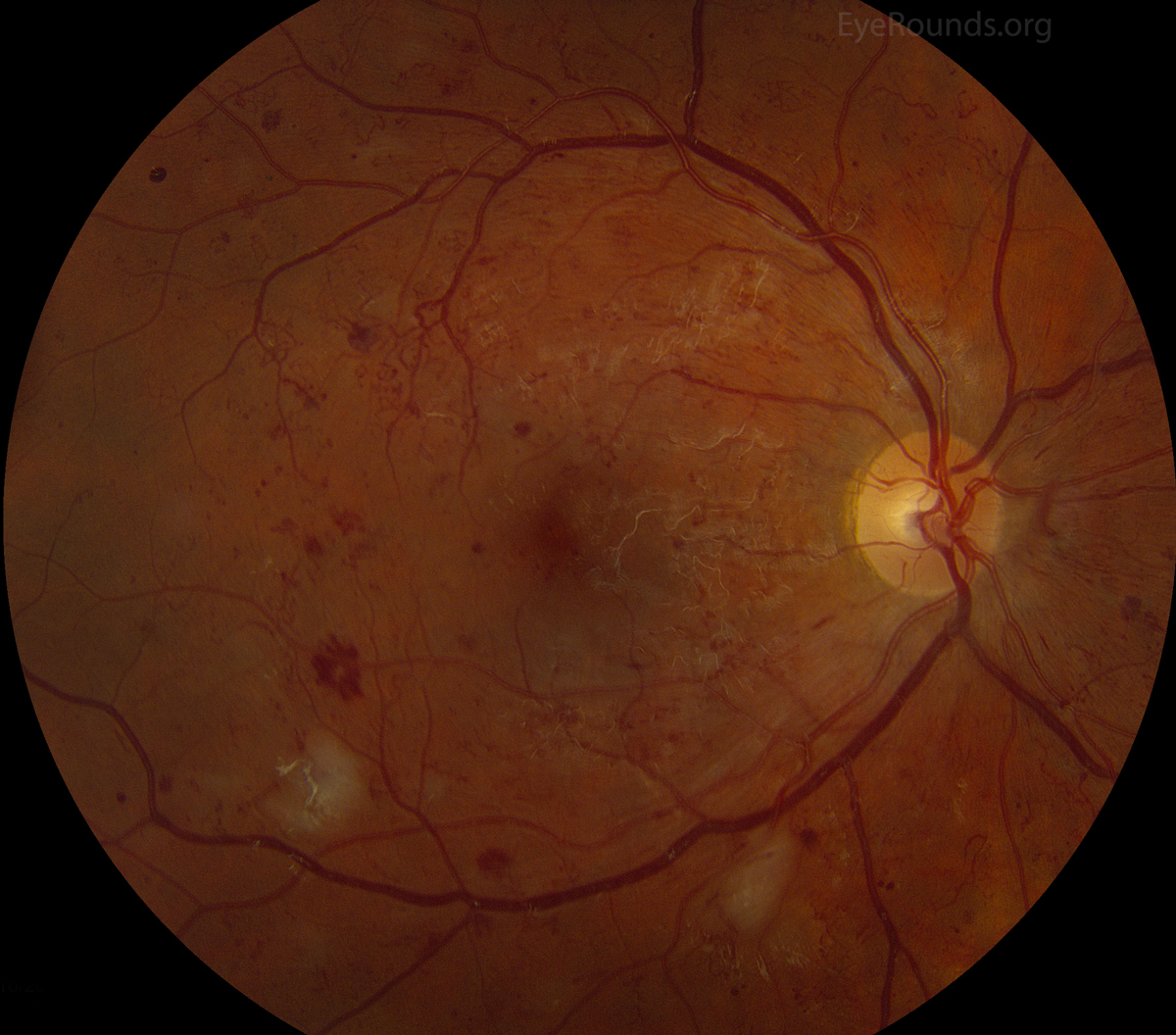



Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormality Irma




Ophthalmology Notes And Synopses Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities Or Irmas Irmas Are Shunt Vessels And Appear As Abnormal Branching Or Dilation Of Existing Blood Vessels Capillaries Within The Retina That Act To
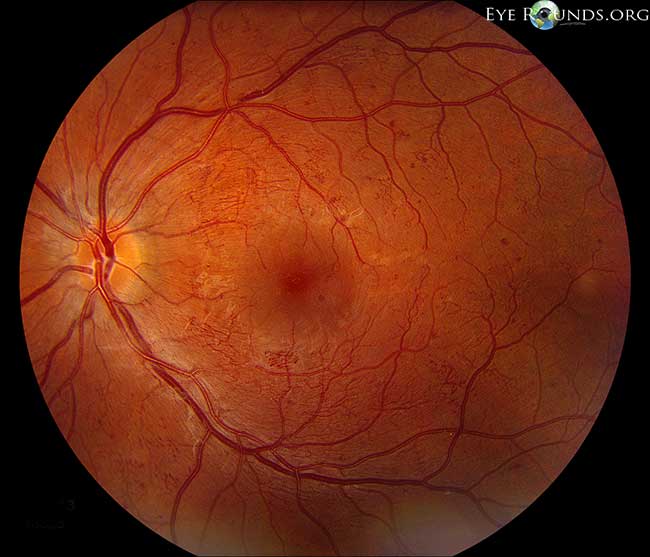



Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormality Irma



Diabetic Eye Screening Services In Scotland A Training Handbook July 03 Page 16
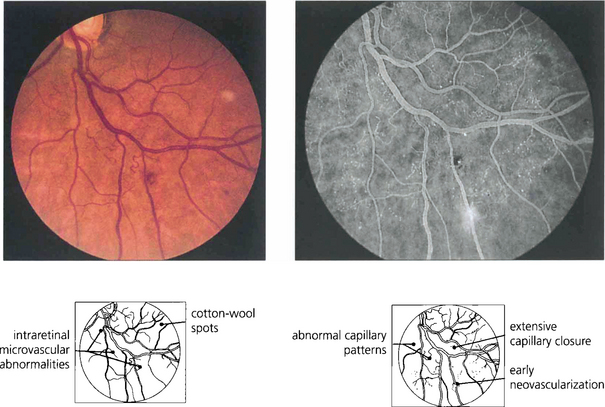



The Retina Vascular Diseases Ii Clinical Gate




How To Diagnose And Manage Diabetic Retinopathy Eyeguru
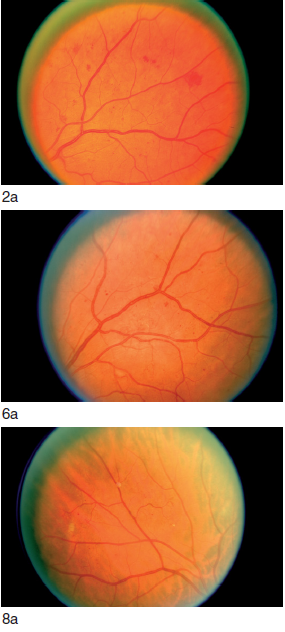



The Retina Diabetic Macular Diease Retina Part 1 Al Salem Eye Clinic



Diabetic Retinopathy Optometry Today




Characteristics Of Neovascularization In Early Stages Of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy By Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography American Journal Of Ophthalmology



Chua Eye Page Atlas Of Diabetic Retinopathy



Using Oct Angiography To Diagnose High Risk Diabetic Retinopathy Retina Today



Diabetes Care In The Age Of Anti Vegf



Diabetic Eye Screening Services In Scotland A Training Handbook July 03 Page 8



Diabetic Eye Screening Services In Scotland A Training Handbook July 03 Page 16




Figure 10 From Clinical Pathology Of Diabetic Retinopathy And Macular Edema Semantic Scholar



Optician



Diabetic And Hypertensive Retinopathy30 3 11 Phpapp01



Diabetes Clinic



Http Www Icoph Org Dynamic Attachments Taskforce Documents Peripheral Grading Chart Pdf



How To Classify The Diabetic Eye American Academy Of Ophthalmology



Discussion And Pictures Of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions



Diabetic Retinopathy Europe American Academy Of Ophthalmology
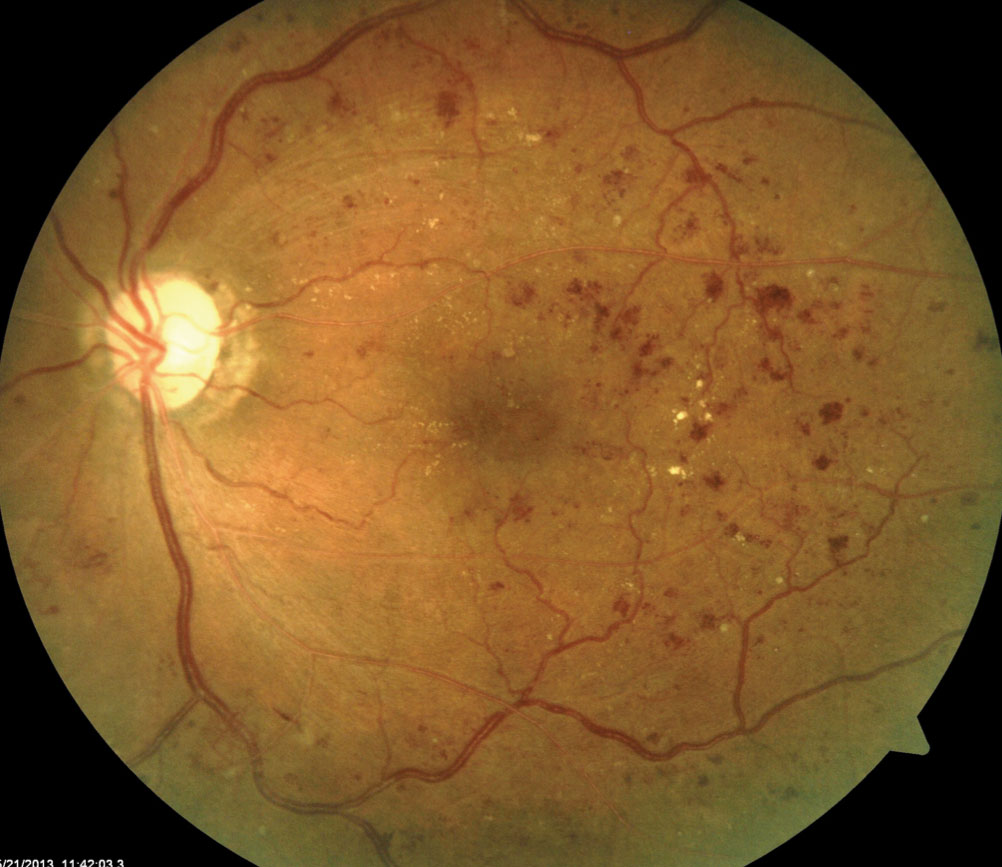



My Patient Has Diabetic Retinopathy Now What
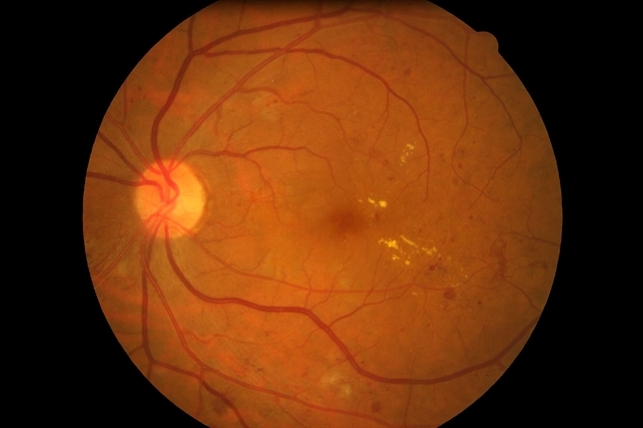



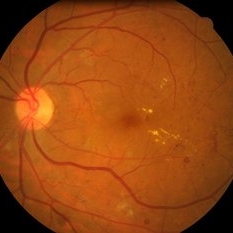
Maculopathy And Irma Left Retina Retina Image Bank
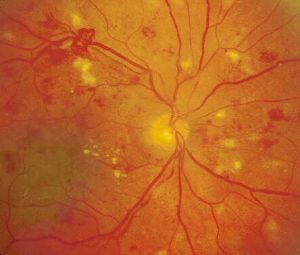



How To Diagnose And Manage Diabetic Retinopathy Eyeguru




Diabetes Photos Flashcards Quizlet
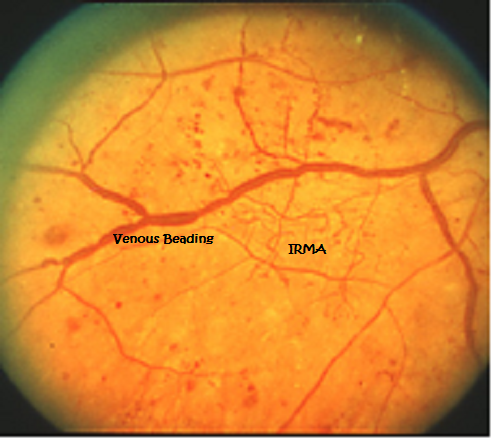



What Is The Difference Between Irma And Neovascularization Irma Example Two Images Questions About Diabetes Related Retinopathy




Characteristics Of Neovascularization In Early Stages Of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy By Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography American Journal Of Ophthalmology
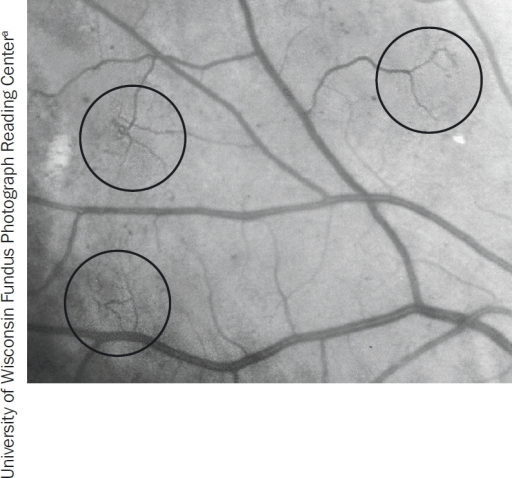



Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irma The Ci Open I
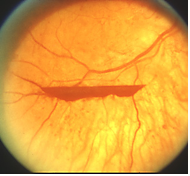



Discussion And Pictures Of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions
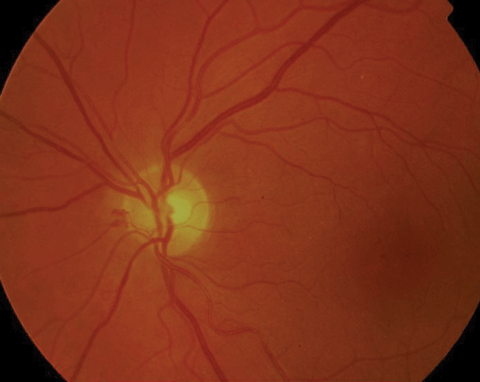



Diabetic Retinopathy By The Numbers
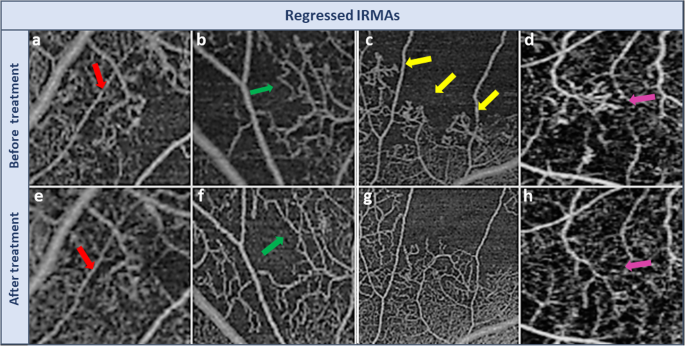



Morphological Changes In Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities After Anti Vegf Therapy Visualized On Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Eye And Vision Full Text
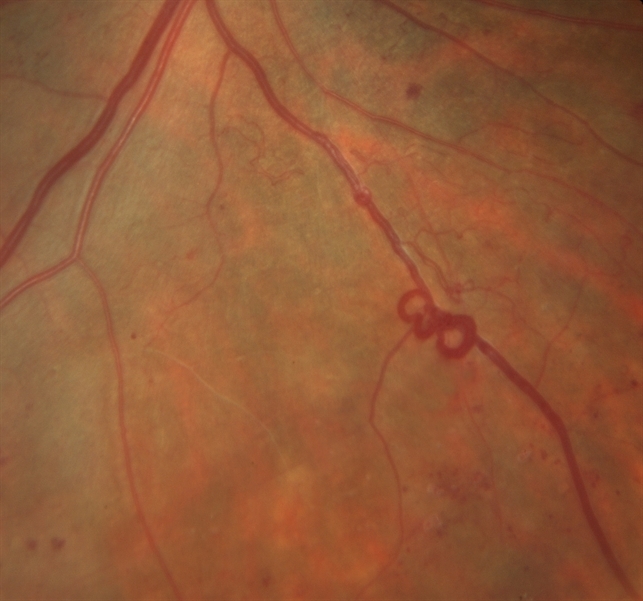



Venous Loop In Severe Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Retina Image Bank




Diabetic Retinopathy Maidstone Eye Practice Diabetic Retinopathy Eye Facts Diabetes



How To Classify The Diabetic Eye American Academy Of Ophthalmology




Screening And Detection Of Diabetic Retinopathy By Using Engineering Concepts Sciencedirect
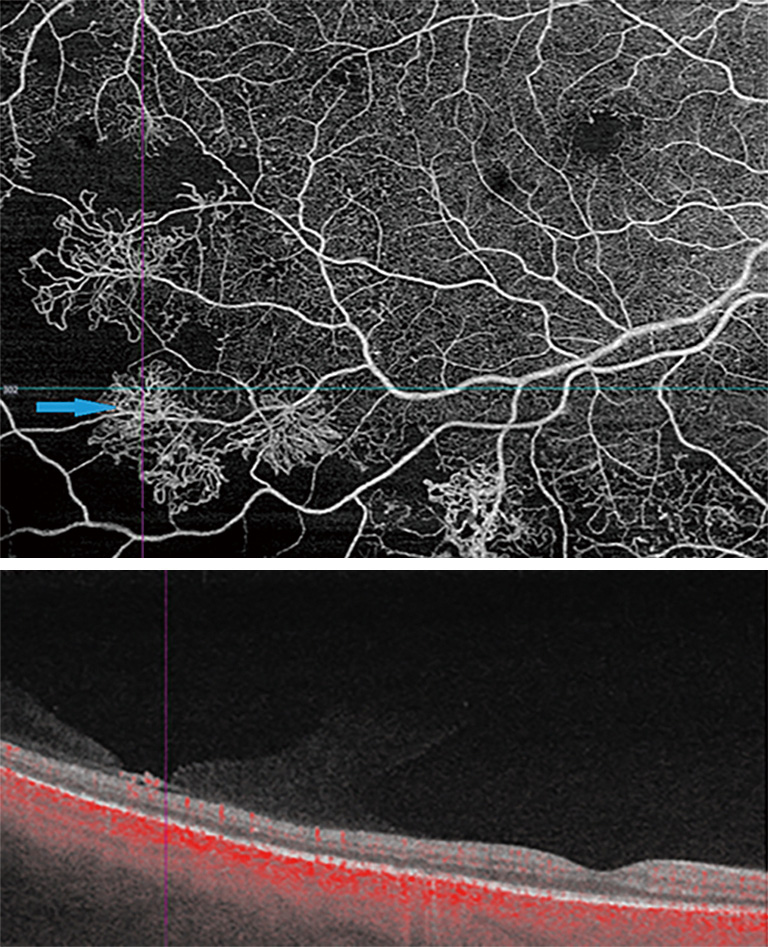



New Findings And Challenges In Oct Angiography For Diabetic Retinopathy Sorour Annals Of Eye Science




Diabetic Retinopathy Features Of Diabetes Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irmas




Ophthalmology Notes And Synopses Facebook




How To Diagnose And Manage Diabetic Retinopathy Eyeguru




Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities Irma American Academy Of Ophthalmology
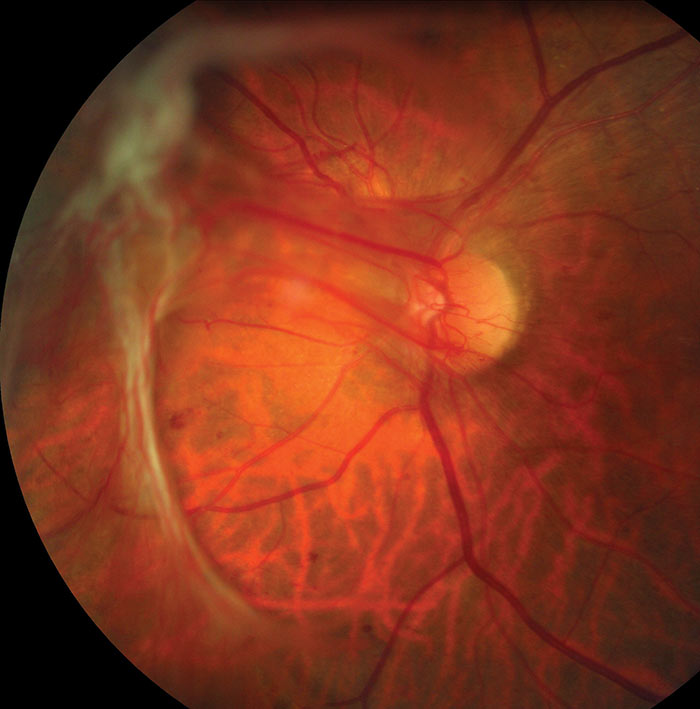



Optician



View Image
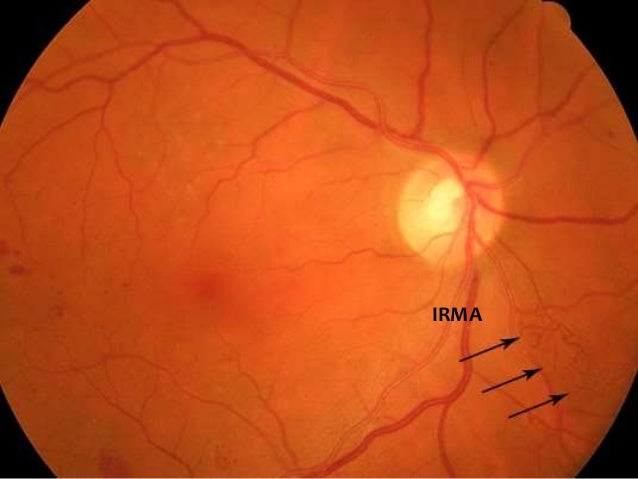



Diabetic And Hypertensive Retinopathy30 3 11 Phpapp01




Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



1
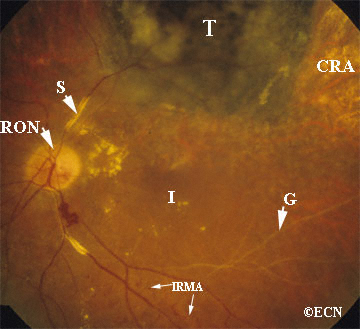



The Finger Classification Of Radiation Retinopathy New York Eye Cancer Center



Aucun commentaire:
Publier un commentaire